
TCP/IP
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol) is a collection of protocols including TCP, IP, UDP, ARP, and others. It was developed by the Department of Defense for the precursor to the Internet. It is an open design, allowing for any company or organization to freely develop products and services based on TCP/IP.
TCP is used to keep the signal error free while IP is responsible for the data packets sent over the network.
TCP/IP is routable, meaning it can span more than one local area network (LAN). Not all protocols are routable, so having TCP/IP be able to carry Network layer addressing information is a benefit and has led to its widespread use. Additionally, TCP/IP supports carrying a wide variety of protocols and services on many different types of media, making it one of the most flexible networking protocols.
TCP
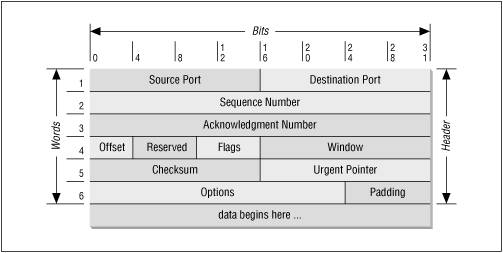
TCP is a connection-oriented protocol requiring an end-to-end communication channel open between two hosts. Connection information, known as a handshake, is exchanged to establish how the two hosts will communicate.
The diagram shows a TCP Segment, the information communicated between the two hosts. It uses a checksum for each host to check to see if the data is undamaged during transit. If the data is damaged, one host can request a retransmit from the source host.
IP
IP, or Internet Protocol, is a data-oriented protocol used for communicating data across a packet-switched internetwork. It is a connection-less network layer protocol which is encapsulated in a data link layer protocol. IP provides the service of communicable unique global addressing amongst computers.
Currently, that definition may have just flown right over your head. When you’re finished with this tutorial, most of that will make sense to you.
IP provides the connection-less delivery service for transport-layer protocols such as TCP and UDP.
IP is similar to sending a letter to a post office box. IP
is the zip code of the post office box, while the port is the post office box number. For example, if you send a letter to PO Box 2448, Columbus, Ohio 43229, the mailman would deliver it to the Post Office at 43229 (the IP address), then the mailman working at the 43229 Post Office would deliver it to the right mailbox (the port).
It is connection-less, so it does not need to maintain a connection to transmit data. IP transmits data in packets, formatted blocks of data.
For the CompTIA Network+ exam, you need to understand the core concepts behind TCP/IP, but you do not need to know in-depth technical information that a CCNA would understand, for example.

