Connect to local and network print devices.
Printing is one of the areas which you will spend a lot of time as a technician. Nothing is more frustrating to users in a hurry than to have a document they need not print off in the time they need it.
In this section, we will review printing, how to install and connect to printers, managing printers, and controlling access to printers.
Connect to a local print device.
The first step to discuss printing is to install a local print device. A local print device could take many forms – an inkjet printer, a local laser printer, or a label printer. The printer could be connected to the machine in a number of ways – USB, parallel, Bluetooth, or infrared.
Most local printers, when connected via USB, will initiate a Plug’n’Play installation of the printer driver. Occasionally, we are required to install the printer manually:
1.Connect the printer to the PC and power both on.
2.Click Start and then Printers and Faxes.

3.Click Add a printer in the taskbar on the left.
4.Click Next.
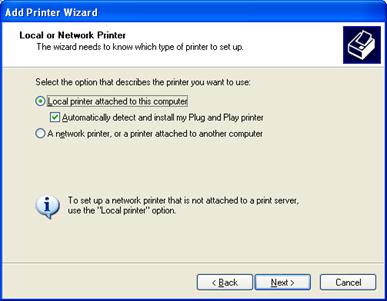
5.Click Next for a local printer attached to the computer.
6.Windows will search for a Plug’n’Play printer. If it does not find one, click Next.
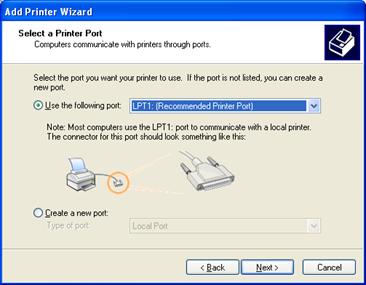
7.Select the port you have the printer plugged into and click Next.
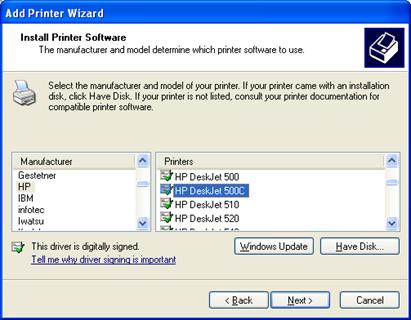
8.Select the Manufacturer on the left and the Printer on the right. Click Next.
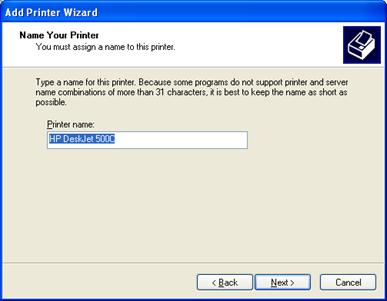
9.Enter a Printer Name. Click Next.
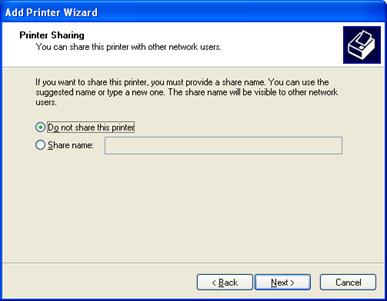
10.If you’d like to share the printer on the network, click on Share name and enter a friendly name. Click Next.
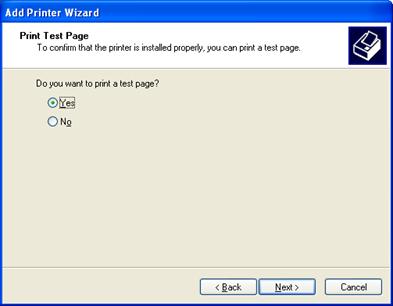
11.If you’d like to print a test page, click Next. Otherwise, click No then click Next.
12.Click Finish to complete the printer install.
13.You now have a printer installed.
Installing Additional Drivers
Microsoft has designed functionality for shared printers which allows you to install additional drivers for Windows NT 4, Windows 2000, 95/98/ME, and others. You can access this functionality by right-clicking on the printer and selecting Properties.
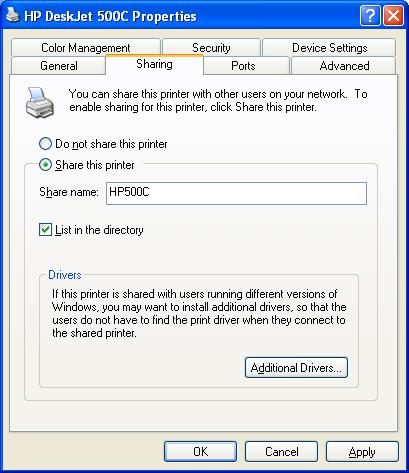
Once in the printer properties, select the Sharing tab and click on Additional Drivers.
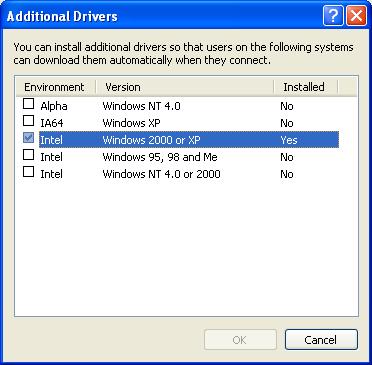
You can select whichever computers you want to support and install drivers for the particular OS.
One thing to note for the exam: Windows NT, 2000, and XP will check for new drivers when it connects to the host machine. Windows 95/98/ME do not check for updated drivers and must be manually updated.

