Administering a Server
There are two typical methods you use to administer a server: locally and remotely. Local administration is often referred to as “console administration.” Remotely you can administer through a remote control package (or the built-in Remote Desktop for Administration) or you can remotely manage the server through Microsoft Management Console (MMC). We explored MMC a little in the previous section. Let’s review:
Microsoft Management Console
Microsoft Management Console (MMC) is the primary administrative tool in Windows Server 2003. It uses snap-ins to configure functions and services of the server. Third parties can design their own MMC snap-ins to manage their products within the MMC framework.
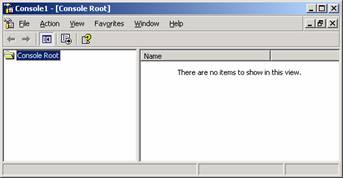
Think of MMC as the shell which allows you to use the snap-ins to manage the server. When you manage a server, you are using the actual snap-ins not MMC itself to manage the server. The screenshot shows an empty MMC console. You can add in any snap-ins you require to administer the server.
Adding a Snap-In
- Click Start, Run, type in mmc and click OK.
- Click the File menu and choose Add/Remove Snap-In.
- The Add/Remove Snap-in window appears. Click Add.
- The Add Standalone Snap-in window appears. In this list are the predefined MMC snap-ins you can use to manage your server. Choose one from the list, such as Active Directory Users and Computers. Click Add.
- You can continue adding additional snap-ins or click Close.
- Click OK.
- The snap-in appears in MMC.
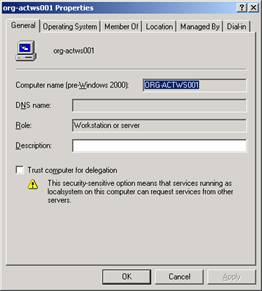
Repeat the same process but choose Computer Management as the snap-in you want to add. When you click Add, the computer selection dialog box appears.
This box allows you to select the local machine or a remote computer to manage. If you select Another computer, you can remotely manage that machine using this console. You must have administrative rights on that machine to manage it.

